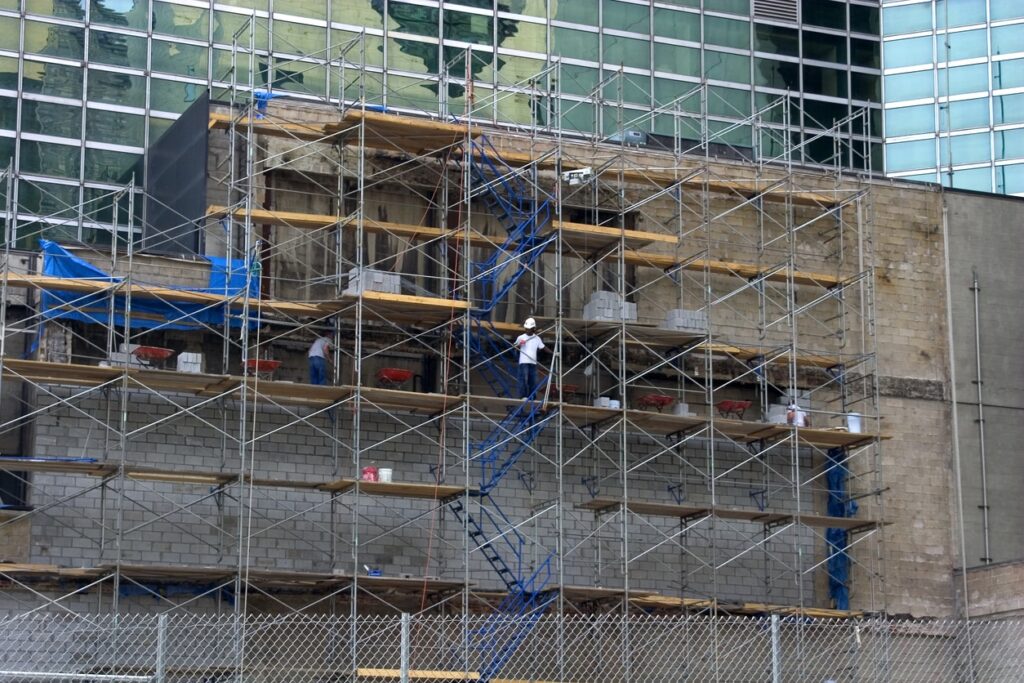
Construction scaffolding is a vital component of any building project, providing essential support and access for workers and materials. However, it also poses significant risks if not properly managed. Understanding the legal considerations and safety measures is crucial to prevent injuries or fatalities on-site.
Construction Work: Key Considerations
- Scaffolding in construction is a critical temporary structure that ensures safe access for workers and materials, particularly in projects involving heights.
- Adhering to safety standards, regular inspections, and innovative technologies in scaffolding is essential for preventing accidents and ensuring a productive work environment.
- Legal implications can arise if scaffolding accidents occur, making it imperative for construction companies to comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations.
Understanding Scaffolds in Construction
Scaffolding construction involves erecting temporary structures that provide secure and stable access for workers performing tasks at elevated heights. This setup not only supports personnel but also facilitates material handling, promoting efficiency and safety on construction sites. Wooden scaffolding, for example, spans distances and minimizes worker movement time, proving indispensable for tall structures or areas with accessibility challenges.
A Temporary Structure: Types of Scaffolding Systems
For nearly every construction project, a temporary structure known as a scaffold may be used. A scaffold consists of numerous parts and can take several forms, including:
Trestle Scaffolding
- Description: Trestle scaffolding involves a framework that rests on movable tripods or ladders, making it suitable for tasks done at lower heights.
- Use Cases: Ideal for interior work, such as painting and minor repairs, where height requirements are minimal.
- Advantages: Simple to set up and lightweight, making it easy to transport and adjust within small or confined areas.
- Limitations: Not suitable for high or heavy-duty work, as it is designed for lower height tasks (usually up to 5 meters).
Bamboo Scaffolding
- Description: Bamboo scaffolding, traditionally used in parts of Asia, is a framework made from bamboo poles tied together, often using plastic or natural ropes.
- Use Cases: Primarily used in regions where bamboo is readily available, and it’s known for being lightweight, flexible, and environmentally friendly.
- Advantages: Bamboo is sustainable, cost-effective, and surprisingly strong, with a high strength-to-weight ratio. Skilled workers can assemble bamboo scaffolding quickly.
- Limitations: It may not meet the stringent safety standards required in some regions, particularly where heavy loads or extreme heights are involved, as it requires skilled handling and regular maintenance.
Steel Scaffolding
- Description: Steel scaffolding consists of steel tubes connected by couplers or fittings, forming a sturdy, durable framework.
- Use Cases: Preferred for heavy-duty construction, particularly on larger buildings and at higher elevations.
- Advantages: Steel scaffolding offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for supporting heavy loads and providing stability. It is also fire-resistant and weather-resistant, which increases its lifespan.
- Limitations: Heavier and more expensive than other materials, and it requires skilled labor for assembly and disassembly. Steel also needs protection from rust if used outdoors in certain climates.
Sectional Scaffolding
- Description: Sectional scaffolding, also known as modular or prefabricated scaffolding, consists of pre-engineered sections that can be easily assembled and disassembled.
- Use Cases: Widely used in construction for both exterior and interior projects, as well as for maintenance work in industrial settings.
- Advantages: Sectional scaffolding is versatile, with parts designed to lock securely into place. Its modular nature allows for quick assembly, easy transport, and the ability to adapt to varying site conditions.
- Limitations: While flexible, the pre-engineered sections may limit custom configurations needed for some complex structures. Additionally, costs can vary based on material and brand.
Suspended Scaffolding
- Description: Suspended from the top of a building via ropes or cables, allowing height adjustment as needed.
- Uses: Ideal for high-rise tasks like window cleaning, painting, and maintenance where ground support isn’t feasible.
- Pros:
- Adjustable Height: Easily raised or lowered.
- Space Efficient: Doesn’t require ground support, great for narrow spaces.
- Cost-Effective: Minimal material compared to full-height ground scaffolds.
- Cons:
- Safety Risks: Requires strict safety protocols due to suspension.
- Weather Limitations: High winds or storms can halt work.
Cantilever Scaffolding
- Description: Supported on one end, extending outwards using beams (needles) anchored to the building.
- Uses: Used above obstacles or in areas where ground scaffolding isn’t possible.
- Pros:
- Great for Constrained Spaces: Effective above busy streets or overhangs.
- Customizable: Adapts to unique building features.
- Cons:
- Complex Setup: Requires precise engineering for stability.
- Higher Costs: Specialized setup increases cost.
- Safety Risks: Stability can be an issue if not properly anchored.
Each scaffolding type has specific benefits and is suited to particular types of projects. The choice of scaffolding often depends on project height, load requirements, budget, and safety regulations. Whether your construction project requires supported scaffold component installation or a more supportive trestle scaffolding, understanding the potential risks can help business owners and construction employees avoid harm.
Legal Considerations in Scaffolding Accidents
When scaffolding accidents occur, legal repercussions can be severe. Construction companies must adhere to OSHA regulations, which mandate that scaffolding must support its own weight plus at least four times the maximum intended load. Failure to comply can lead to legal action if someone is injured or killed.
Liability and Compliance
Construction firms are responsible for ensuring that scaffolding is erected, used, and dismantled in compliance with safety standards. If negligence is proven, companies may face lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage. Proper documentation and adherence to safety protocols are essential in mitigating legal risks.
Worker Compensation and Legal Rights
In the event of an injury or fatality, affected workers or their families may be entitled to compensation. Understanding legal rights and available recourse is crucial for construction workers. Employers must provide adequate training and safety equipment to minimize risks and protect themselves from potential legal claims.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Safety standards and regulations are essential for maintaining safe scaffolding sites. They cover issues from load capacities to safety barriers, with worker safety being the primary concern.
Approximately 65% of construction workers use scaffolds regularly, contributing to about 4,500 annual injuries. Adhering to safety standards and regulations minimizes these risks and ensures a safe working environment.
OSHA Guidelines
Safety regulations stipulated by OSHA mandate that scaffolding must be capable of carrying not only its own weight but also at least four times the maximum load it is intended to hold. To safeguard workers from fall hazards, employers are required to supply appropriate safety gear such as harnesses and lanyards, as well as implement protective barriers like guardrails and toeboards.
To avoid mishaps involving scaffolding, comprehensive training on its erection, utilization, and dismantling is vital for all involved personnel. Seeking advice from an expert can offer valuable insights while ensuring adherence to established safety standards. Conducting routine inspections and abiding by OSHA guidelines plays a critical role in preserving workplace safety for those working with or around scaffolding.
Understanding the legal considerations and safety measures associated with construction scaffolding is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring compliance with regulations. By prioritizing safety and adhering to legal standards, construction companies can protect their workers, avoid legal repercussions, and maintain a safe and productive work environment.
Is Your Construction Project Safe?
As a construction company owner, ensuring scaffolding safety involves a combination of regular inspections, adherence to safety standards, and proactive maintenance. Here’s a checklist to help you keep your scaffolding safe and free from defects:
- Daily Inspections: Have a competent person inspect scaffolding daily before work begins, checking for any damage, loose components, or wear. Inspections should also occur after any incident, high winds, or extreme weather.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Follow OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) or local safety standards, which specify load limits, guardrails, access points, and other essential requirements. Meeting these standards ensures the scaffolding is structurally sound.
- Routine Maintenance and Repairs: Immediately repair any signs of wear, corrosion, or defects. Maintain a log of all repairs, maintenance, and adjustments to track scaffold safety history.
- Proper Assembly and Dismantling: Ensure trained and experienced workers handle scaffolding assembly and dismantling according to manufacturer guidelines. Improper setup is a leading cause of scaffold failures.
- Weight Limits and Load Management: Adhere to weight limits specified by the scaffolding manufacturer, including workers, tools, and materials. Overloading scaffolding can lead to structural instability.
- Safety Training for Workers: Train workers on proper scaffold use, safety practices, and emergency procedures. They should be familiar with recognizing hazards and using personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriately.
- Regular Third-Party Inspections: For additional assurance, consider having periodic inspections by a third-party safety expert to identify potential issues that may be overlooked during routine checks.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Keep detailed records of all inspections, maintenance, and certifications. Documentation is key for both safety compliance and liability protection.
These steps will help ensure your scaffolding is secure, reducing risks for both employees and bystanders.
Hurt in a Construction Work Accident? Call the Law Office of Nicholas E. Tzaneteas Today
If you are a construction worker, you know that scaffolds are part of nearly every job site. Whether you have to deal with suspended scaffolding, cantilever scaffolding, or steel scaffolding and the assorted cross braces and steel tubes that go into those temporary structures, the risk of severe injury looms large over the site.
If you or someone you love has been injured in a scaffolding accident on a job site, call the Law Office of Nicholas E. Tzaneteas today. As an experienced personal injury attorney, Mr. Tzaneteas can help you protect your rights as you seek fair compensation for your injuries and lost wages. Commercial projects are the source of hundreds of claims in the New York City area every year; take control over your rights if you were injured through no fault of your own.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main legal considerations for scaffolding in construction?
The main legal considerations include compliance with OSHA regulations, ensuring scaffolding can support the required load, and providing adequate safety training and equipment to workers.
How can construction companies mitigate legal risks associated with scaffolding?
Construction companies can mitigate legal risks associated with scaffolding by implementing a comprehensive safety and compliance strategy. This involves several key actions:
Adherence to Safety Standards
Ensuring compliance with OSHA regulations and other relevant safety standards is paramount. This includes verifying that scaffolding systems are capable of supporting their own weight plus at least four times the maximum intended load. Regular updates on safety standards and integrating them into daily operations can significantly reduce legal risks.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Conducting routine inspections and maintenance of scaffolding structures is crucial to identify and rectify potential hazards. Inspections should be thorough, covering all scaffold components such as cross braces, vertical posts, and base plates. Documenting these inspections can serve as evidence of proactive safety measures in the event of legal scrutiny.
Comprehensive Training Programs
Providing comprehensive training for construction workers on the proper erection, use, and dismantling of scaffolding is essential. Training should cover the use of safety equipment, recognition of potential hazards, and emergency response procedures. Well-trained workers are less likely to be involved in accidents, thereby reducing legal liabilities.
Detailed Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintaining thorough documentation of all safety protocols, training sessions, and inspection reports is critical. This documentation can protect companies from potential lawsuits by demonstrating a commitment to safety and compliance. It also aids in identifying areas for improvement in safety practices.
Implementation of Advanced Safety Technologies
Incorporating innovative safety technologies, such as digital monitoring systems and automated inspection tools, can enhance safety measures. These technologies provide real-time data on scaffold integrity and worker safety, allowing for prompt intervention if issues arise.
By prioritizing these actions, construction companies can effectively mitigate legal risks, protect their workers, and maintain a safe and compliant work environment.
What should workers do if injured in a scaffolding accident?
In the unfortunate event of a scaffolding accident, workers should prioritize their health and safety by seeking immediate medical attention to address any injuries sustained. Prompt medical evaluation is crucial not only for health reasons but also for documentation purposes, which can be vital in any subsequent legal proceedings.
Once medical needs are addressed, workers should report the incident to their employer as soon as possible. This report should include detailed information about the accident, including the time, location, and circumstances surrounding the incident. Accurate reporting helps ensure that the incident is properly documented and investigated, which is essential for both health and safety compliance and potential insurance claims.
Understanding legal rights is another critical step. Workers may be entitled to pursue compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and other damages resulting from the accident. It is advisable for injured workers to consult with a legal professional who specializes in workplace injuries to explore their options for compensation. This may involve filing a workers’ compensation claim or pursuing other legal avenues if negligence is a factor.
Additionally, workers should cooperate with any investigations conducted by their employer or relevant safety authorities, such as OSHA, to help determine the cause of the accident and prevent future occurrences. By taking these steps, injured workers can protect their health, assert their rights, and contribute to a safer working environment for all construction workers.






